X-linked Hypophosphatemia (XLH) is a rare, lifelong genetic disorder. It affects the bones, muscles, and teeth of both children and adults. This rare condition is caused by a mutation in the PHEX gene. This leads to abnormal phosphate metabolism in the body. The excessive loss of phosphorus can result in weak bones, which can cause a range of symptoms.
What is X-Linked Hypophosphatemia?
XLH is a disease that gets progressively more severe as time goes on. This is caused by to mutation in PHEX. This is also noted due to the over-secretion of the hormone fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23). The FGF23, in turn, leads to excessive renal phosphate excretion or wasting which results in low phosphorus levels in the blood (hypophosphatemia). Phosphorus plays an important role in bone health, energy for growth, and strengthening teeth.
Key Points about XLH:
- It is an inherent condition, with its origin from X chromosome inheritance.
- It can affect children or adults but with varying symptoms and progression.
- XLH can also be referred to by other names such as X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets and hereditary hypophosphatemic rickets.
How Does XLH Affect the Body?
XLH primarily affects bone health because of phosphorus deficiency. Phosphorus is important for:
- Bone growth and strength
- Energy for normal growth
- Strengthening teeth
Signs & Symptoms of XLH:
XLH symptoms vary from person to person. Signs and symptoms can occur at any age. The condition can affect the bones, muscles, and teeth. This may lead to several complications.
Symptoms in Children:
- Children with XLH often show early signs of the disease:
- Rickets (weakening of growing bones)
- Osteomalacia (weakening of mature bone)
- Delayed walking or difficulty with balance
- Short stature
- Bowed legs or knock knees
- Bone and joint pain
- Dental issues, such as abscesses and tooth loss
- Gait abnormalities (irregular walking pattern)
- Headaches due to Chiari malformations
- Fatigue
Symptoms in Adults:
Symptoms may persist or change as children with XLH grow older. Adults with XLH may experience:
- Bone and joint pain
- Short stature
- Bowed legs or knock knees
- Osteomalacia (weakened bones)
- Hardening of ligaments and tendons (enthesopathy)
- Osteoarthritis (joint damage)
- Pseudofractures (areas of weakened bone)
- Hearing loss
- Fatigue
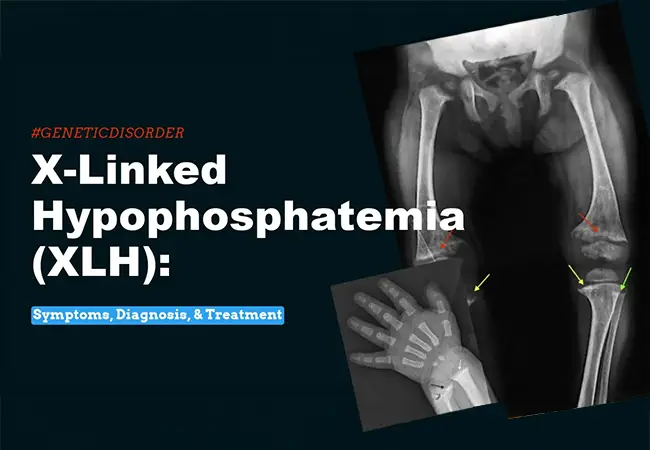
Diagnosis of X-Linked Hypophosphatemia:
Diagnosing XLH early is very important for effective management. It is generally diagnosed in childhood, around the age of 1-2 years, when children start to walk. Because XLH is rare, often with subtle symptoms, delays in diagnosis can occur.
Diagnostic Process:
- A healthcare provider (HCP) will usually recommend the following tests for diagnosing XLH:
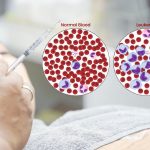
- Blood tests to check phosphorus levels in the body
- X-rays to examine the bones for any health issues and other abnormalities.
- Genetic testing to confirm the availability of mutations in the PHEX gene
Family History:
Because XLH is passed down through families, doctors will also ask about the person’s family’s medical history. This might help determine if anyone else in the family has had such symptoms.
Role of Genetic Counseling:
Genetic counseling can assist you if you or any of your family members are diagnosed with it by helping you with:
- know the inheritance pattern
- assess the risk for other family members
- learn about the available treatment and management options
Treatment and Management of XLH:
XLH can be managed effectively. Treatment options are available to manage the symptoms and improve quality of life (QoL). Treatment typically involves addressing low phosphorus levels, managing pain, and improving bone health.
Treatment Goals for Children:
- Normalize phosphorus levels to promote healthy bone growth
- Heal rickets and osteomalacia
- Prevent bone deformities (like bowed legs)
Treatment Goals for Adults:
- Normalize phosphorus levels
- Heal osteomalacia and prevent fractures
- Relieve pain and improve mobility
Treatment Options for XLH:
Phosphate Supplements and Vitamin D: Traditional treatment involves phosphate supplements combined with vitamin D. They were the first line of treatment. This increases phosphorus levels in the patient’s body while also improving the bone strength. This, however, may not be useful in the long term for many people.
Burosumab (The Latest Treatment): Burosumab is the most exciting advancement in XLH treatment. It is a monoclonal antibody that is designed to block the activity of FGF23, the hormone responsible for phosphorus loss. It is an FDA-approved medicine for XLH treatment. It is available for patients aged 6 months and older. Burosumab is designed to restore normal phosphorus levels and improve bone health.
Benefits of Burosumab:
- It is designed to assist in correcting phosphorus level in the blood.
- It treats osteomalacia and increases bone health
- It decreases the likelihood of developing pseudofractures along with other skeletal complications.
Pain Control and Supportive Treatment: Managing bone pain, joint function, and mobility for XLH adults are parts of joint treatment. Musculoskeletal conditions may require physical therapy along with pain management approaches aimed at symptom relief.
Living with X-Linked Hypophosphatemia:
XLH is a lifelong condition, but with appropriate treatment and care, a patient with XLH can live a meaningful life. Osteoanabolism and phosphaturic osteomalacia are two accompanying bone disorders. In tandem with other HCPs, regular monitoring of these parameters is crucial. Moreover, dietary selections and restricted high-impact exercise practices can be effective in lessening bone strain.
Key Takeaways:
- XLH is a genetic disorder that is both rare and complex characterized by a deficiency of phosphorus affecting bones, teeth, and muscles.
- Symptoms in children include osteomalacia, rickets, and delayed walking.
- In adults: complications may include osteoarthritis and pseudofractures.
- Blood tests, X-rays, and genetic testing enable early diagnosis to assist in effective management.
- Treatments like Burosumab are designed to help normalize phosphorus levels and improve bone health.
In which countries Crysvita is approved?
Crysvita has been approved for use in several countries worldwide, including the United States, Canada, and the European Union (which also covers Norway, Iceland, and Liechtenstein). It is also approved in Brazil, Japan, Switzerland, South Korea, Australia, and New Zealand. Other countries where Crysvita has received approval include Mexico, Turkey, UAE, Argentina, Colombia, and Chile. For patients in India who require Crysvita, the Indian Pharma Network (IPN) facilitates the import of this medicine from these approved countries.
Where can I buy Crysvita injection in India?
You can buy Crysvita injection online in India from the Indian Pharma Network (IPN), a reliable importer and supplier. IPN ensures easy access to Burosumab (Crysvita) for patients in need across the country.
Who is the supplier of Crysvita in India?
Indian Pharma Network (IPN) is a leading supplier of Crysvita in India. We provide high-quality Burosumab (Crysvita) injections to meet the needs of patients and healthcare professionals (HCPs) in the country.
How can I get Crysvita imported to India?
Indian Pharma Network (IPN) is a trusted Crysvita importer in India. We can help you import Burosumab (Crysvita) injections from countries where this medicine is available and approved. We ensure compliance with regulations and timely delivery.
Is Crysvita available in India through the Indian Pharma Network?
Yes, the Indian Pharma Network (IPN) is a reliable supplier and importer of Crysvita in India. We provide legal access to Burosumab (Crysvita) injections. We provide the availability of Crysvita for patients requiring treatment for X-linked hypophosphatemia.