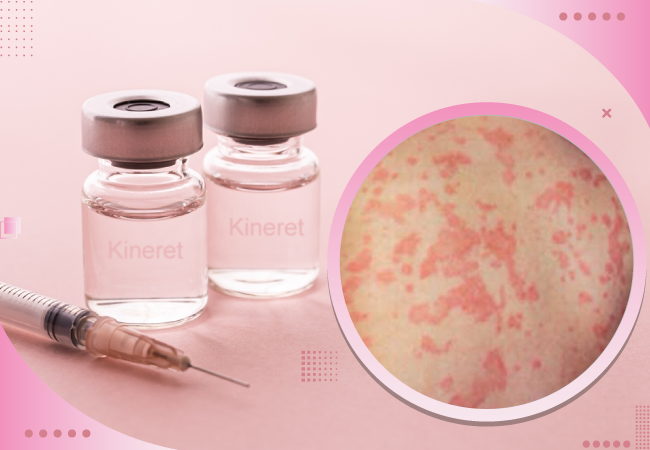
Neonatal-onset multisystem Inflammatory Disease (NOMID) is a rare and severe autoinflammatory disorder that affects multiple organ systems, presenting a myriad of challenges for patients and healthcare professionals. One of the treatments showing promise in managing the symptoms of this complex condition is a medication known as Kineret. Let’s delve into the overview of NOMID in the context of Kineret and understand how this medication offers hope for those grappling with this condition.
Understanding NOMID and Its Symptoms
NOMID is characterized by fever, skin rashes, joint inflammation, and inflammation of various organs, including the central nervous system (CNS). All patients with NOMID develop skin rashes during infancy, which persist throughout their lives. Additionally, CNS symptoms such as chronic aseptic meningitis, cognitive impairments, seizures, and sensory organ dysfunction can lead to complications like vision and hearing loss.
The Role of Kineret in Treating NOMID
Kineret, or anakinra, is a medication used to treat adult rheumatoid arthritis, an immune system disorder that causes joint inflammation. In the context of NOMID, it offers a glimmer of hope for patients battling this rare condition. Kineret is classified as an interleukin-1 (IL-1) inhibitor, which means it targets the cytokine responsible for triggering inflammation. It is administered in combination with the anti-inflammatory drug methotrexate and is specifically prescribed to patients who haven’t responded well to methotrexate alone.
FDA Approval and Other Treatment Options
In 2013, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) granted approval to Kineret, marketed by Sobi, Inc., as a treatment for individuals with NOMID. It remains the only FDA-approved drug for managing this condition. Additionally, other medications such as canakinumab (Ilaris) and rilonacept (Arcalyst) have been explored for treating CAPS, including NOMID, although they haven’t received specific FDA approval for NOMID treatment.
A Glimpse of Hope
NOMID is a challenging condition that can severely impact the quality of life for affected individuals. The emergence of Kineret as a viable treatment option provides a glimpse of hope for patients and their families. By targeting the inflammatory processes underlying the disease, Kineret aims to alleviate symptoms and improve the overall well-being of NOMID patients.
Conclusion
NOMID presents a unique set of challenges due to its complex and multi-systemic nature. Kineret’s emergence as an FDA-approved treatment for NOMID offers a promising avenue for managing the symptoms of this rare disorder. With ongoing research and advancements in medical science, treatments like Kineret underscore the progress being made in addressing rare and complex conditions, bringing hope and improved outcomes to those affected by NOMID.