Nelarabine, also known as Atriance or Arranon, is a type of chemotherapy drug that belongs to the group of antineoplastic agents. These therapeutic drugs work by destroying certain cancer cells, making them effective for specific types of cancer. Nelarabine is primarily used to treat T-cell cancers, particularly T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) and T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma (T-LBL).
Indications:
Nelarabine is administered via injection to treat:
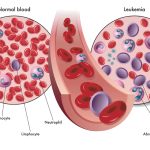
T-cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (T-ALL): This type of leukemia causes a sharp increase in immature white blood cells called lymphoblasts in the blood and other body areas, impairing the immune system.
T-cell Lymphoblastic Lymphoma (T-LBL): This type of lymphoma involves a mass of lymphoblast cells and impacts white blood cells known as T-cells, affecting the body’s lymphatic system.
Mode of Action:
Nelarabine is a pro-drug, meaning it is inactive until processed within the body. Once activated, it interferes with DNA synthesis in cancer cells, leading to their destruction. Nelarabine gets converted to ara-GTP, which integrates into the DNA of cancer cells, stopping their growth and eventually leading to cell death.
Dosage and Administration:
- Adults: The usual dose is 1,500 mg/m² given intravenously over two hours on Days 1, 3, and 5 in a 3-week cycle.
- Pediatrics: For children, the recommended dose is 650 mg/m² given intravenously over 60 minutes daily for five consecutive days in a 3-week cycle.
Treatment duration depends on factors like patient response, disease progression, or suitability for bone marrow transplantation.
Common Side Effects:
Nelarabine’s side effects can vary between adults and children:
Adults: Common side effects include fatigue, blood disorders (like anemia and low platelets), gastrointestinal issues (nausea, vomiting, diarrhea), nervous system symptoms (dizziness, drowsiness), respiratory problems (cough, shortness of breath), and fever.
Pediatrics: Children may experience low potassium levels, headache, low albumin, high bilirubin, vomiting, and elevated liver enzyme levels.
Precautions and Contraindications:
- Hypersensitivity: Nelarabine should not be used in individuals with known allergies to any of its ingredients.
- Tumor Lysis Syndrome: This condition can arise from the rapid breakdown of cancer cells, releasing their contents into the bloodstream. Patients on Nelarabine may need hydration and preventive medication to manage this syndrome.
- Seizures: Nelarabine has been linked to seizures in some patients, so health providers should closely monitor for neurological symptoms.
- Blood Monitoring: Blood counts, especially platelets and white cells, should be checked regularly to manage blood-related side effects.
- Vaccinations: Patients on Nelarabine should avoid live vaccines, as their immune response may be weakened, increasing infection risk.
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding:
Nelarabine is classified as a pregnancy Category D drug, indicating a potential risk to a fetus. Women of childbearing age should use effective birth control to avoid pregnancy. Breastfeeding mothers are advised not to nurse during treatment due to possible drug transfer through breast milk.
Drug Interactions:
Nelarabine may interact with adenosine deaminase inhibitors (such as pentostatin), which can interfere with its conversion to the active form. Patients should discuss all medications, supplements, and any vaccinations with their healthcare provider to avoid adverse interactions.
Conclusion:
Nelarabine shows promising results in treating relapsed or treatment-resistant T-cell leukemia and lymphoma, especially as a third-line therapy. It’s commonly used in combination with other chemotherapy agents for improved outcomes. Neurological side effects, however, are a significant consideration, and a “black box” warning highlights these risks. Patients undergoing Nelarabine treatment need careful monitoring for signs of neurotoxicity.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
What types of cancer does Nelarabine treat?
Nelarabine is used for T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) and T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma (T-LBL). It’s effective in killing cancer cells by disrupting their DNA synthesis.
How is Nelarabine administered?
Nelarabine is given through intravenous infusion in cycles, with adults typically receiving it on Days 1, 3, and 5 of each 3-week cycle, while children usually receive it daily for five days in each 3-week cycle.
Can you send Nelarabine to a foreign destination?
Yes, the Indian Pharma Network facilitates the supply of Nelarabine to countries where it’s not approved, including Brazil, UAE, Argentina, Mexico, Saudi Arabia, Egypt, Turkey, Vietnam, Thailand, South Africa, and Nigeria. Send your inquiry today via Call/WhatsApp: +91 9310090915 to buy Nelarabine from India.
Are there any precautions while using Nelarabine?
Yes, patients need regular blood monitoring, should avoid live vaccines, and are advised to manage tumor lysis syndrome with hydration. Those who experience neurological symptoms, like seizures, should contact their healthcare provider.
Can Nelarabine be used during pregnancy?
Nelarabine is not recommended during pregnancy due to potential risks to the fetus. Women of childbearing age should use effective contraception during treatment.
Disclaimer:
This article provides general information and should not replace the guidance of a qualified healthcare provider. Patients should consult their doctor for personalized advice and treatment.