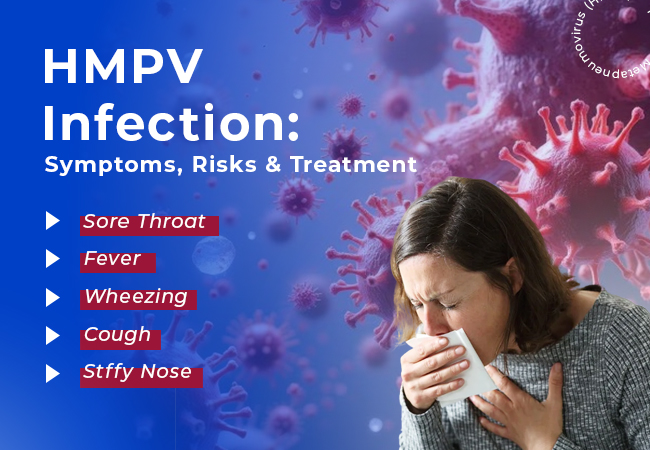
Human metapneumovirus (HMPV) is one of the common respiratory viruses from the Pneumoviridae family known for causing mild colds or even severe lung infections such as pneumonia and bronchiolitis. Though not famous like influenza or RSV, HMPV has a reputation all on its own as a serious contributor to respiratory illnesses around the globe, especially during the winter and spring seasons.
HMPV presents a substantial risk to certain populations, including young children, elderly individuals, pregnant women, and those with weakened immune systems. Raising awareness and implementing preventive measures are important to mitigating its effects.
Vulnerable Populations at Risk for HMPV:
- Infants and Toddlers: It is important to note that young children are at a higher risk of severe respiratory conditions such as bronchiolitis and pneumonia.
- Elderly Individuals: Adults aged sixty-five and above, as well as people with chronic illnesses such as asthma or Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), are more likely to experience complications.
- Expectant Mothers: It is especially fatal to HMPV expectant mothers as it is hard for them to breathe which puts not just them but the baby at serious risk.
- Immunocompromised Patients: People receiving treatment that weakens their immune system like chemotherapy or individuals suffering from immune conditions tend to experience the brunt of the symptoms.
Recent HMPV Outbreak in China:
A recent surge of HMPV cases in China has drawn attention to its severity, particularly in young children. Most infections have been reported in children aged under 14 years, with numerous hospitalizations due to serious signs and symptoms. Common symptoms included fever, persistent cough, bronchiolitis, and pneumonia.
Diagnosing and treating HMPV can be challenging because its signs and symptoms closely mimic other respiratory infections. In response, Chinese health authorities have emphasized the importance of regular hand washing, wearing masks, and conducting tests for possible HMPV infections.
Recognizing Symptoms of HMPV in Adults and Children:
Symptoms in Adults:
- persistent cough, often with mucus production
- nasal congestion or a runny nose
- mild to moderate fever
- fatigue and body aches
- sore throat
- shortness of breath in more severe cases
Symptoms in Children:
- difficulty breathing
- wheezing and prolonged
- coughing
- high fever
- poor feeding and
- dehydration, particularly in infants
Modes of Transmission of HMPV:
HMPV is a highly infectious disease and spreads through several common pathways:
- Respiratory Droplets: Respiratory processes such as talking, coughing, and sneezing will cause droplets to spread into the air containing the virus.
- Physical Contact: Touching an infected person and then touching the eyes, mouth, or nose can lead to infection.
- Contaminated Surfaces: The virus can persist on surfaces for long periods increasing the chances of transmission from shared items like cell phones or door knobs.
- Airborne Particles: Tiny particles containing respiratory droplets hold in the atmosphere for an extended period. This is especially true in areas that are densely populated and poorly ventilated.
How is HMPV Diagnosed?
Because the symptoms exhibited by HMPV are almost of all other respiratory infections, laboratory tests are mandatory for an exact diagnosis
- HMPV PCR Test: This test identifies the viral genes and is hence most accurate in diagnosing HMPV.
- Rapid Antigen Tests: These tests are not as precise as PCR tests, however, they can provide results much quicker.
- Bronchoscopy: This is useful in monitoring changes in the airways of severely infected patients.
Complications Linked to HMPV:
The majority of people suffering from HMPV get better within the span of a week to a week and a half without facing kidney issues. However, worst-case complications can occur in high-risk individuals.
- Pneumonia: Severe cases can lead to viral pneumonia that may at times require a hospital visit.
- Bronchiolitis: Toddlers and small children can suffer from airway swelling that will make it hard for them to breathe.
- Aggravation of Chronic Conditions: Those suffering from asthma or extreme cases of COPD may show worsened signs.
- Secondary Bacterial Infections: Complications can lead to bacterial pneumonia and ear infection.
- Pregnancy-Related Risks: Health problems may arise for both the mother and child during pregnancy that can stem from respiratory infections.
Available Treatments for HMPV:
Currently, there are no particular antiviral medicines for HMPV. The treatment roster available for this virus includes managing the signs and symptoms to improve the quality of life along with ensuring no complications arise:
- Rest and Hydration: Recovery is quickly expedited through ample amounts of sleep and hydration.
- Over-the-Counter Medications: Fever reducers can help patients who struggle with high body temperatures and excruciating pain; acetaminophen or ibuprofen are often used for this purpose.
- Oxygen Therapy: Patients suffering from severe conditions may require oxygen therapy or even a ventilator.
- Hospitalization: If a patient suffers from severe secondary complications like pneumonia, then they may need to be put under strict medical assistance.
Preventive Measures Against HMPV:
HMPV does not have an effective vaccine available which is why procedures to eliminate exposure to the virus are recommended:
- Practice Proper Hygiene: Wearing a mask to properly cover your mouth and nose while using soap to wash your hands, or: 20 seconds is the minimum time suggested to wash hands skin deep to ensure cleanliness.
- Avoid Close Contact: Keeping a distance from people who are coughing or showing other signs of infection is recommended, along with not visiting crowded places especially when many people are infected.
- Disinfect Frequently Touched Surfaces: Clean commonly used items such as doorknobs, phones, and countertops regularly.
- Wear Masks: To help eliminate the chance of catching infections during the flu season or other outbreak periods wearing masks in public spaces is encouraged.
- Self-Isolation When Sick: Staying at home is the easiest way to not spread an infection if you are showing signs of a virus.
Conclusion:
As is, the knowledge of HMPV is vital for early intervention and effective control. Knowing its symptoms, risk factors, and how it spreads enables people to guard against it and get the necessary medical help where necessary.
How does HMPV differ from other respiratory viruses like RSV or influenza?
HMPV and RSV have commonalities in the bronchiolitis and pneumonia they cause in young children. Still, HMPV has far graver consequences for older immunocompromised patients. On the other hand, there is no vaccine or specialized antiviral treatment provisions for HMPV similar to flu.
When should I consider testing for HMPV?
Severe HMPV test-positive respiratory symptoms, recent exposure to an already infected individual, and belonging to any high-risk group would all recommend testing.
Can HMPV cause long-lasting symptoms?
Generally, most subjects fully recover within a 1-2 week span. However, pneumonia and other complications can hamper the recovery rate for many from the particularly vulnerable groups.
Are antibiotics useful in treating HMPV?
The viral nature of HMPV renders the use of antibiotics futile. There is always a chance, however, of antibiotics being prescribed if the patient suffers from subsequent secondary complications due to bacterial infection.
What risks does HMPV pose to pregnant women?
HMPV remains a potentially complicated virus with multifaceted challenges for pregnant women. Nowadays many pregnant women are exposed to unmonitored high-risk work environments such as hospitals which increases the risk for respiratory illnesses that can complicate maternal and fetal health. Proper precautions such as universal hygiene and minimal exposure to the ill can be helpful.
How does HMPV impact children?
HMPV remains a prime candidate for the etiology of bronchiolitis and pneumonia in young children. Signs and symptoms of the infection can sometimes include wheezing, shortness of breath, fever, and a combination of dehydration which may make hospital admission necessary.
Can HMPV lead to long-term complications?
Some variants of the virus, especially those that initiate pneumonia, might remain as an underlying source for respiratory problems later in life, chronic respiratory tract illnesses, exacerbated asthma, or other respiratory conditions.
Can a person get HMPV multiple times?
Yes, there exists no protective immunity from HMPV which allows the virus to be reinfected.
What is the primary source of the HMPV?
It is assumed that HMPV is derived from birds and later adapted to infect humans. HMPV was first captured in surveillance in 2001 and is believed to have been present for several decades without being discovered.
Can HMPV cause vomiting, diarrhea, or ear infections?
Secondary bacterial infections can occur and while vomiting and diarrhea are atypical, they have been observed in extreme instances.