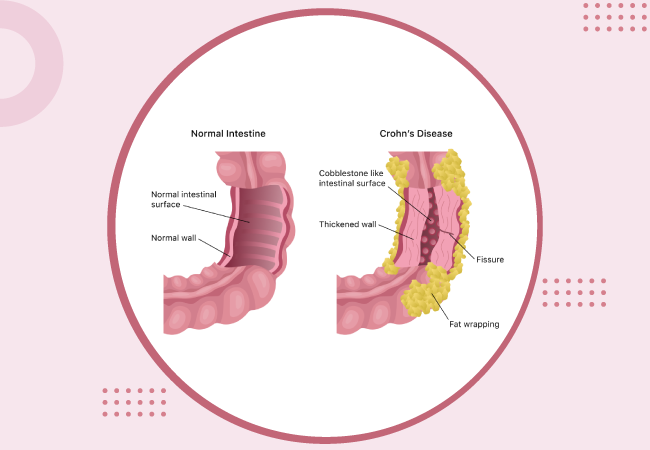
Crohn’s disease is a chronic, or long-term inflammatory disorder that affects the GI tract (gastrointestinal tract, digestive tract). According to Crohn’s and Colitis Foundation, Crohn’s disease falls under the group of health conditions known as IBD or inflammatory bowel diseases. The disease is named after Dr. Burrill B. Crohn, who first stated it back in 1932 along with his colleagues, Dr. Gordon D. Oppenheimer and Dr. Leon Ginzburg.
Health specialists still aren’t exactly certain what causes Crohn’s disease, but it occurs because of an overreaction of the immune system in the gastrointestinal tract. Crohn’s disease can affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract from your mouth to your anus, but it most frequently affects the small intestine and the starting of the colon.
There are different sorts of Crohn’s disease, depending on where in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract the condition affects individuals. Because there are different types of Crohn’s, the signs and symptoms will also vary.
Types of Crohn’s Disease:
While signs and symptoms of Crohn’s disease can vary from patient to patient, the sort of Crohn’s you have affects the symptoms and complications you may suffer.
Ileocolitis: Occurs most commonly, it affects the terminal ileum (the end of the small intestine), and the colon (large intestine). Symptoms of Ileocolitis may include:
- Diarrhea and cramping
- Abdominal pain
- Weight loss
Ileitis: It typically affects only the ileum. Symptoms of Ileitis may include:
- Diarrhea and cramping
- Abdominal pain
- Weight loss
- Fistulas or inflammatory abscesses in the abdomen
Gastroduodenal Crohn’s Disease: It affects the stomach and the starting of the small intestine, known as the duodenum. Symptoms of this type may include:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Weight loss
- Loss of appetite
Jejunoileitis: In this form, the patchy portions of inflammation in the jejunum (second portion of the small intestine) occurs. Symptoms of Jejunoileitis may include:
- Mild to intense abdominal pain/cramps after meals
- Diarrhea
- Fistulas may develop in serious cases
Crohn’s (Granulomatous) Colitis: It affects only the colon, called the large intestine. Symptoms of Crohn’s (Granulomatous) Colitis may include:
- Diarrhea
- Rectal bleeding
- Disease around the anus, including ulcers, abscesses, and fistulas
- Joint pains and skin lesions are more common
Conclusion:
Crohn’s disease can be cured. Available medicines and other therapeutic options, including diet and lifestyle changes can help cope with symptoms. The disease often occurs in cycles of remission and flare-ups, so therapeutic plans will need re-assess and monitoring. Crohn’s treatment is individualized, so what is useful for anyone else may not be useful for you and vice versa. Work with your clinician to come up with a therapeutic plan to cope with the symptoms of Crohn’s disease.
Reference:
https://www.crohnscolitisfoundation.org/what-is-crohns-disease
https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/crohns-disease/definition-facts